What opportunities and challenges does the rise of new energy vehicles bring to the electronic components market
The rapid rise of new energy vehicles, especially the popularity of electric vehicles (EVs), has brought huge opportunities and challenges to the electronic components market. The following is a detailed analysis:
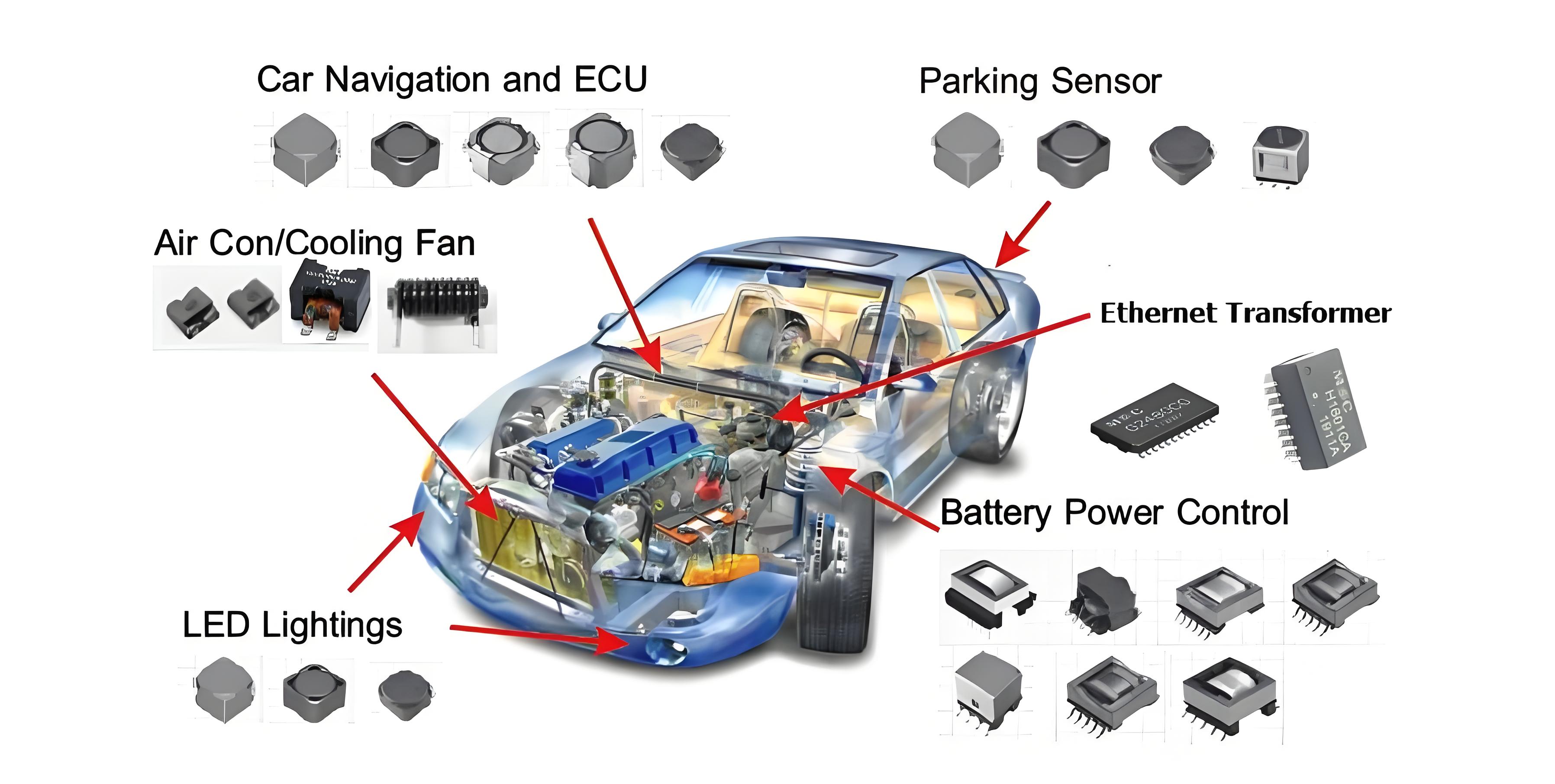
Opportunities
1. Surge in market demand
The core of new energy vehicles relies on electronic control systems, battery management systems (BMS), drive systems and charging infrastructure, and the demand for electronic components has surged:
Power semiconductors: The application of MOSFET, IGBT and SiC (silicon carbide) devices in new energy vehicles has grown significantly due to their key role in inverters, charging modules and motor drives.
Sensor market expansion: The demand for current, temperature, pressure and speed sensors has increased rapidly to meet the requirements of new energy vehicles for real-time monitoring and precise control.
Control chips: The demand for high-performance chips such as MCU, DSP, FPGA has increased for control systems, BMS and communication modules.
Passive components: The demand for capacitors, inductors and transformers has increased, especially film capacitors and high-voltage ceramic capacitors for high-frequency and high-voltage scenarios.
2. New materials technology promotes
wide bandgap semiconductors: SiC and GaN (gallium nitride) devices are gradually replacing traditional silicon-based devices due to their high efficiency, high frequency and high voltage resistance, especially in fast charging and high-performance inverters.
Lightweight materials: Coils and heat sinks used in new energy vehicles drive the demand for lightweight materials (such as aluminum instead of copper).
3. Supporting industry chain development
Charging infrastructure: The popularization of DC fast charging and wireless charging technology requires a large number of electronic components, such as power devices, filters and communication modules.
Internet of vehicles and autonomous driving: New energy vehicles integrate more intelligent functions (such as on-board AI, OTA updates, ADAS), and the demand for communication chips, radar sensors and computing platforms is growing rapidly.
4. Policy and capital support
Government subsidies for new energy vehicles, restrictions on carbon emission standards, and the capital market's investment boom in green energy have provided development opportunities for electronic component manufacturers.
Challenges
1. Increased technical threshold
The complexity of new energy vehicle systems is much higher than that of traditional fuel vehicles, which places higher demands on electronic components:
High reliability and durability: Power devices must withstand high temperature, high pressure, high frequency and harsh environment.
Miniaturization and integration: More functions need to be integrated in a limited space, forcing components to develop in the direction of miniaturization and multi-function.
Safety standards: Especially BMS and drive circuits, higher requirements are placed on electrical safety (such as overcurrent and overtemperature protection).
2. Cost pressure
Raw material price fluctuations: For example, the limited supply of rare earth elements and wide bandgap semiconductor materials has led to high costs.
Intense market competition: Industry giants and start-ups have entered one after another, and price wars may affect profit margins.
3. Supply chain pressure
Chip shortage: The global semiconductor shortage directly affects the production of new energy vehicles, especially key components such as MCU and power devices.
Logistics and delivery: The impact of the epidemic and geopolitical risks have increased supply chain uncertainty.
4. Uncertainty of technical routes
Standards and compatibility:
Charging standards of different countries and manufacturers (such as CHAdeMO, CCS, GB/T) have not yet been fully unified, which may lead to the complexity of component design.
Risk of technological change:
Wide bandgap semiconductors gradually replace traditional silicon-based devices, requiring manufacturers to find a balance between R&D investment and production line upgrades.
5. Environmental protection and regulatory pressure
Environmental protection requirements: The production of electronic components must meet stricter environmental protection regulations (such as RoHS, REACH).
Recycling and sustainable development: The growth of electronic waste brought by new energy vehicles has driven the electronic component industry to develop in the direction of recyclability and degradability.
Coping strategies
How companies can seize opportunities
Strengthen R&D investment: especially in the fields of wide bandgap semiconductors, high-density packaging and intelligent control.
Optimize supply chain management: Establish a localized supply chain and improve risk resistance.
Diversified layout: Explore related fields of vehicle electronics, charging infrastructure, and energy storage markets.
Challenges faced by the industry
Jointly formulate standards: Promote the global unification of charging protocols and electronic components.
Green production: Promote clean production technology to reduce the impact on the environment.
Talent cultivation: To meet the technical needs of the new energy vehicle industry, we will accelerate the training of high-end electronic engineers and technicians.
The rise of new energy vehicles will drive innovation and growth in the electronic components market in the long term, while also requiring companies to continuously improve their technology and adaptability to the rapidly changing market environment.