[ Component Knowledge ] Main Types and Applications of Gyroscope Sensor Chips
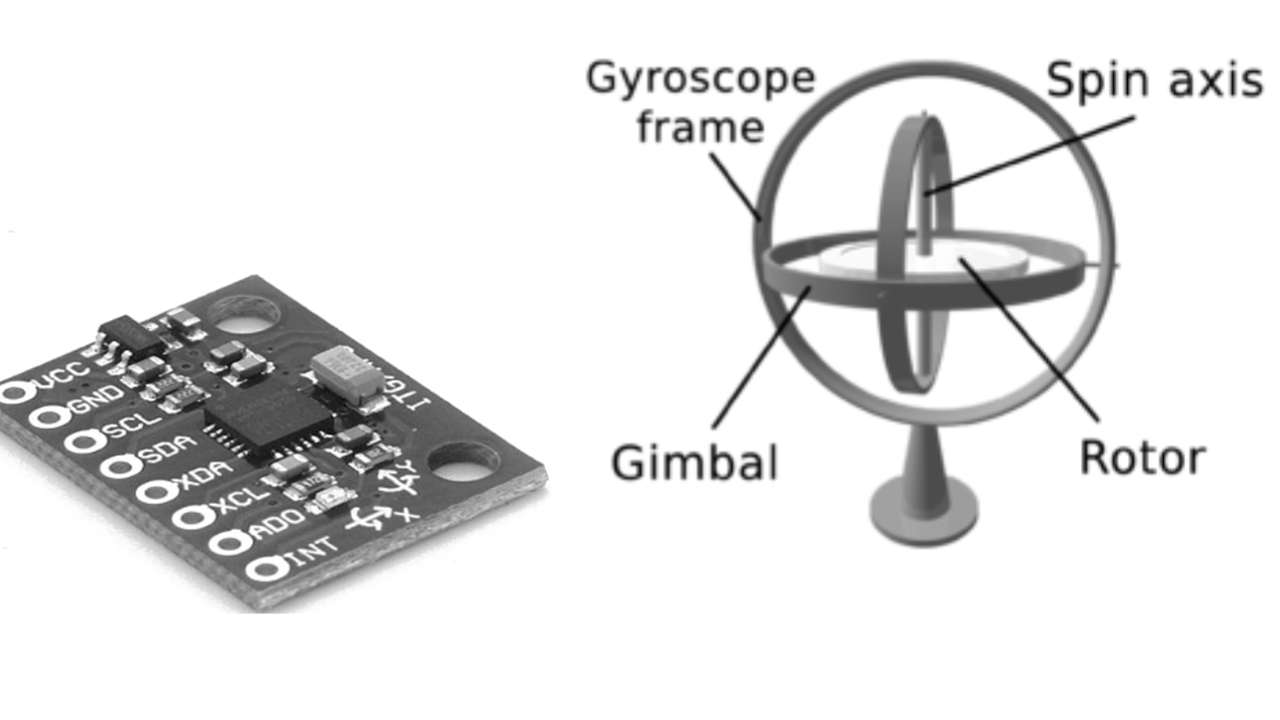
As the core component of the inertial measurement unit (IMU), gyroscope sensors play a key role in navigation, robotics, games and consumer electronics. Its function is to measure the angular velocity of an object and use it to infer the change in the object's posture, providing important data support for positioning, motion tracking and stability control. According to its internal working principle, gyroscope sensor chips can be mainly divided into the following types:
Microelectromechanical system (MEMS) gyroscope
Working principle: Use the Coriolis force generated by the micromechanical structure during rotation to determine the angular velocity by detecting the magnitude of the force.
Function and application: It has the advantages of small size, low power consumption and low cost. It is widely used in consumer electronic products such as mobile phones, game consoles, tablets, etc. to realize functions such as automatic screen rotation and somatosensory operation in games; in the field of automotive electronics, it is used for vehicle stability control systems, navigation systems, etc.; in drones, it is used to measure the angular rate of rotation of the body around its own axis to help maintain a stable flight attitude. However, its accuracy is relatively low and is easily affected by temperature drift.
Fiber Optic Gyroscope (FOG)
Working Principle: Using the Sagnac effect, two beams of light are propagated in the optical fiber loop in clockwise and counterclockwise directions respectively, and the angular velocity is calculated by measuring the propagation time difference between the two beams of light.
Function and Application: It has the advantages of high precision and strong anti-interference ability. It is often used in aerospace, military and other fields with extremely high precision requirements, such as the inertial navigation system of aircraft and missiles, which can provide accurate attitude and heading information for aircraft to ensure the accuracy and safety of flight.
Ring Laser Gyroscope (RLG)
Working Principle: Using the Sagnac effect, but its optical path is not in the optical fiber, but directly in the ring resonator, and the angular velocity is calculated by measuring the frequency difference of two counter-propagating laser beams in the cavity.
Function and Application: It has high precision and high reliability, and is mainly used in navigation and strategic navigation systems, such as ship navigation systems, which can provide accurate attitude and heading information for ships in complex marine environments to ensure safe navigation of ships; it is also used in the navigation systems of some high-end weapons and equipment. However, it is large in size and has a high cost.
Quartz flexible accelerometer gyroscope
Working principle: Based on the piezoelectric effect of quartz crystal, the angular velocity is determined by measuring the electrical signal generated by the flexible vibration of the quartz crystal.
Function and application: It has the advantages of high precision, low drift, and strong impact resistance. It is often used in inertial navigation systems, such as navigation control of missiles and satellites. It can provide stable and accurate attitude and angular velocity information in complex flight environments to ensure the precise guidance and stable flight of aircraft.
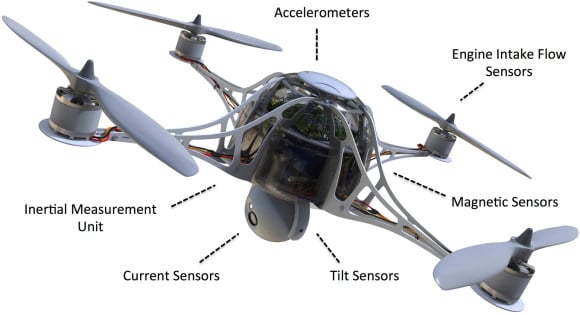
Application of gyro sensors in drones
Which type of gyroscope sensor chip has the highest accuracy?
Among the common types of gyroscope sensor chips, fiber optic gyroscopes (FOG), ring laser gyroscopes (RLG) and quartz flexible accelerometer gyroscopes can usually achieve high accuracy. It is generally believed that ring laser gyroscopes have the highest accuracy. The details are as follows:
Ring laser gyroscope: The accuracy can reach 0.001°/h~0.01°/h, or even higher. Its random drift is less than 0.001 degrees per hour, the long-term accuracy stability is good, the output has no change in 9 years, and the repeatability is excellent. It has no moving parts, no mass imbalance problem, is not sensitive to the vibration and impact acceleration of the carrier, and the output signal has no cross-coupling terms. It can provide high-precision attitude and heading information for navigation and strategic navigation systems. However, it is large in size and expensive.
Fiber optic gyroscope: The accuracy can usually reach the tactical level to the navigation level, and can be used in aerospace, military and other fields with high precision requirements. Compared with the ring laser gyroscope, its accuracy is slightly lower, and the accuracy of some products is about 1°/h, but there are also high-precision models that can approach the accuracy of the ring laser gyroscope. It has the advantages of compact structure, high sensitivity, strong anti-interference ability, and reliable operation. It has replaced mechanical traditional gyroscopes in many fields.
Quartz flexible accelerometer gyroscope: It has the advantages of high precision, low drift, and strong impact resistance. It is often used in inertial navigation systems, such as navigation control of missiles and satellites. Although the accuracy is also very high, it is usually slightly inferior to the absolute value of the accuracy index of the ring laser gyroscope and some high-precision fiber optic gyroscopes.
Micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) gyroscope: The accuracy is relatively low, usually in the order of 1°/h~10°/h. However, with the development of technology, some high-performance MEMS gyroscopes have reached navigation-level accuracy, and the main technical indicators are in the same echelon as those of international mainstream manufacturers, but overall, there is still a certain gap in accuracy compared with the previous high-precision gyroscopes. Its advantages are small size, low power consumption, low cost, strong environmental adaptability, easy mass production, and wide application in consumer electronics, automotive electronics and other fields.
In addition, the nuclear magnetic resonance gyroscope and atomic interferometer gyroscope, which are in the research stage, aim to achieve high-precision, high-reliability, miniaturization and navigation systems in a wider range of applications. They may have higher accuracy performance in the future, but they are not yet mature.

How to choose the right gyroscope sensor chip?
Choosing the right gyroscope sensor chip requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors. The following are some key points:
Application scenarios
Consumer electronics: such as mobile phones, game consoles, etc., are usually cost-sensitive and require low power consumption and small size. MEMS gyroscopes are ideal. For example, MPU6050 is integrated into a variety of consumer-grade IMU modules to meet basic attitude detection and somatosensory interaction needs.
Aerospace and military: Fiber optic gyroscopes, ring laser gyroscopes, or quartz flexible accelerometer gyroscopes are often used for high accuracy and reliability. For example, inertial navigation systems of aircraft and missiles, high-precision fiber optic gyroscopes or ring laser gyroscopes are required to ensure accurate control of flight attitude and heading.
Automotive electronics: Used in vehicle stability control systems, navigation systems, etc., which require both certain accuracy and adaptability to the working environment of the car, such as temperature changes and vibrations. MEMS gyroscopes can meet general needs, and some high-end car autonomous driving systems may use gyroscopes with higher accuracy.
Robotics: Different types of robots have different requirements for gyroscopes. Industrial robots usually require high-precision gyroscopes to ensure the accuracy of motion control. MEMS gyroscopes or quartz flexible accelerometer gyroscopes can be selected; while service robots, sweeping robots, etc. are more sensitive to cost, and general MEMS gyroscopes can meet the needs of attitude detection and path planning.
Performance parameters
Accuracy: including indicators such as resolution, zero bias, and nonlinear error. The higher the resolution, the smaller the minimum angle change that can be detected; the smaller the zero bias, the higher the stability of the output when static; low nonlinear error means that the linear relationship between the output and the actual angular velocity is good, and the measurement is more accurate. For example, in drones that require precise attitude control, gyroscope chips with high accuracy, low zero bias and nonlinear error should be selected.
Range: Select a gyroscope with a suitable range based on the maximum angular velocity that may occur in the application. For example, some drones will generate a large angular velocity when maneuvering at high speed, so it is necessary to select a gyroscope with a larger range for accurate measurement.
Frequency response: A gyroscope with high frequency response can quickly track changes in angular velocity and is suitable for scenarios where the motion state changes frequently and quickly, such as the dynamic motion process of a robot or high-speed flight attitude changes in aerospace.
Temperature drift: A gyroscope with small temperature drift can maintain good accuracy and stability under different temperature environments. For devices that work in a wide temperature range, such as automobiles and outdoor robots, it is crucial to choose a gyroscope chip with low temperature drift.
Interface type
SPI: It has high-speed data transmission capabilities and is suitable for scenarios where gyroscope data needs to be read quickly, such as industrial control and robotic applications with high real-time requirements.
I2C: The interface is simple and occupies few pins. It is often used in cost- and complexity-sensitive fields such as consumer electronics. Multiple sensors can be connected to the microcontroller through the same bus.
Power consumption
For battery-powered devices, such as mobile robots and drones, low-power gyroscope chips can extend the battery life of the device, so it is necessary to choose a gyroscope with low power consumption to reduce the consumption of battery power.
Cost
On the premise of meeting performance requirements, cost is an important consideration. MEMS gyroscopes are relatively low-cost and suitable for large-scale applications in consumer electronics and some cost-sensitive fields; while fiber optic gyroscopes, ring laser gyroscopes, etc. are technically complex, have high manufacturing process requirements, and are expensive. They are mainly used in aerospace, military and other fields that have extremely high precision requirements and are not very sensitive to cost.
Size and packaging
When the equipment space is compact, it is necessary to choose a gyroscope chip with a small package. For example, some miniaturized MEMS gyroscopes use surface mount technology (SMT) packaging, which can save circuit board space and is suitable for portable devices and small robots.
Brands and suppliers
Choose products from well-known brands and reliable suppliers, and their product quality, technical support and after-sales service are more guaranteed. For example, STMicroelectronics (ST), Bosch, Analog Devices (ADI), etc. have rich experience and good reputation in the field of sensors.
Different types of gyroscope sensor chips have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of accuracy, volume, power consumption and cost. Choosing the right type of gyroscope requires comprehensive consideration based on the needs of specific application scenarios to achieve the best performance and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the various types of gyroscopes and their functions is essential for developing efficient and reliable navigation and control systems.
As a professional electronic component distributor, Dasenic provides a variety of gyroscope sensor chips